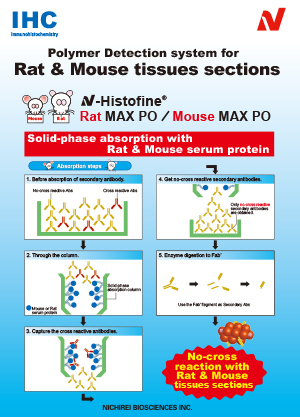
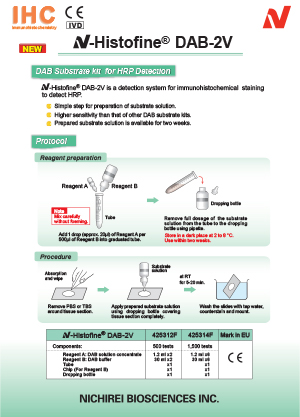
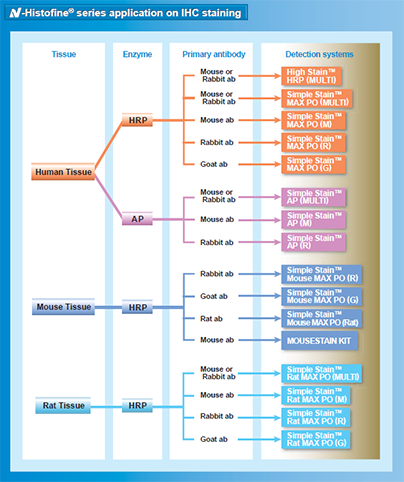
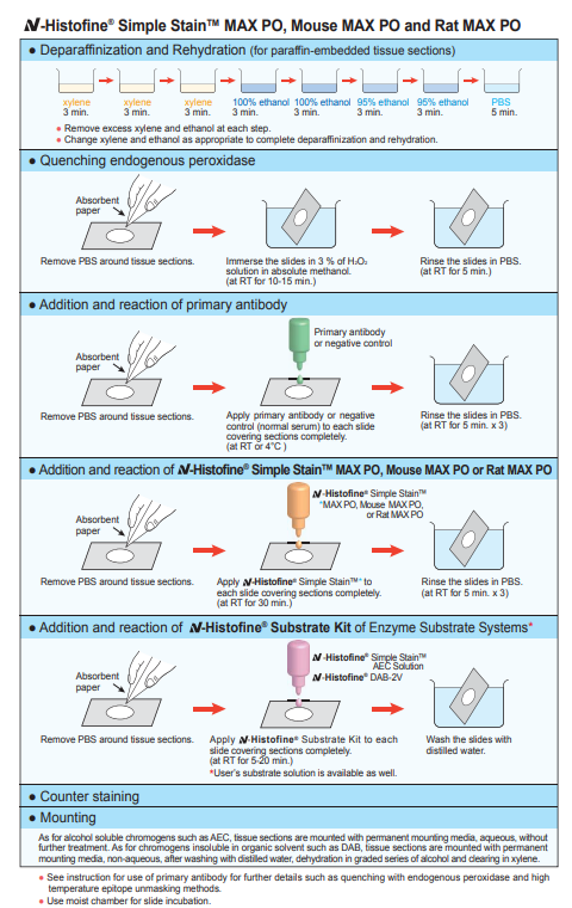
| Problem |
Possible Case |
Solution |
| 1. |
No staining or only weak staining results on the positive control slide and the unknown specimen slide. |
|
| 1) |
Drying-out of specimens during staining prior to addition of the reagents. |
|
| – |
Never allow the tissue to dry out. |
|
| 2) |
The embedding agent is not suitable, or paraffin is not thoroughly removed from paraffin-embedded sections. |
|
| – |
Select a suitable embedding agent or remove paraffin thoroughly from sections embedded. |
| – |
Change xylene or ethanol as the case may be. |
|
| 3) |
Any trace amount of sodium azide present in the buffer inactivates the peroxidase, making the staining impossible. |
|
| – |
Use sodium azide free buffer solution. |
| – |
Change buffer solution. |
|
| 4) |
Inadequate incubation of the enzyme and antibody. |
|
| – |
Change stale chromogen/substrate reagent. |
| – |
Blot off excess solution thoroughly at each stage. |
| – |
Provide sufficient time for reaction with antibody. In particular, primary antibody should be incubated for the time period specified in the insert. |
|
| 2. |
The unknown specimen slide is not stained while the positive control slide is stained. |
|
| 1) |
Antigen is denatured or masked during fixing or embedding process. |
|
| – |
Some antigens are sensitive to fixation or embedding. So use less potent fixative and decrease the fixing time. |
| – |
The pretreatment is required for some tissues, in order to reveal the antigen, such as Antigen Recovery, Heat-Induced Epitope Retrieval or trypsin treatment. |
|
| 2) |
Antigen is decomposed by autolysis. |
|
| – |
Use tissues obtained by biopsy or surgery, whenever possible. |
|
| 3. |
The backgrounds are intensively stained in all the slides. |
|
[ Peroxidase staining ]
| 1) |
Endogenous enzyme activity was not completely blocked. |
|
| – |
Ensure the treatment with 3% of hydrogen peroxide added methanol to inactivate endogenous peroxidase activity. |
|
| 2) |
Non-specific staining is found. |
|
| – |
Before adding primary antibody, treat with 10% normal goat or rabbit serum as follows. |
| Product name |
Serum |
Simple StainTM MAX PO (M)
Simple StainTM MAX PO (R)
Simple StainTM MAX PO (MULTI) |
goat
goat
goat
|
| Simple StainTM MAX PO (G) |
rabbit |
Simple StainTM Mouse MAX PO (R)
Simple StainTM Mouse MAX PO (G)
Simple StainTM Mouse MAX PO (Rat)
|
goat
rabbit
goat
|
Simple StainTM Rat MAX PO (M)
Simple StainTM Rat MAX PO (R)
Simple StainTM Rat MAX PO (G)
Simple StainTM Rat MAX PO (MULTI) |
goat
goat
rabbit
goat
|
|
|
[ Alkaline phosphatase staining ]
| 1) |
Endogenous enzyme activity was not completely blocked. |
|
| – |
Add Levamisole to chromogen/substrate solution. To reduce endogenous enzyme activity, chromogen/substrate solution containing 1mM Levamisole is used. |
|
| 2) |
Non-specific staining is found |
|
| – |
Before adding primary antibody, treat with 10% normal goat serum. |
| Product name |
Serum |
Simple StainTM AP (M)
Simple StainTM AP (R)
Simple StainTM AP (MULTI) |
goat
goat
goat |
|
|
| 3) |
Autolysis results in excessive antigens isolated in histological solutions. |
|
| – |
Obtain fresh tissues whenever available. |
|
| 4) |
Insufficient removal of paraffin. |
|
| – |
Change xylene or ethanol as the case may be. |
|
| 5) |
Insufficient washing of antibody. |
|
| – |
Ensure thorough washing of antibody. |
|
| 6) |
A high room temperature accelerates enzyme reactions. |
|
| – |
Keep room temperature at 15 to 25°C. |
| – |
Shorten reaction time of enzyme. |
|
| 7) |
Drying-out of specimens during staining after addition of the reagents. |
|
| – |
Never allow the tissue to dry out. |
|
| 4. |
During the reaction, tissue sections come off from the slides. |
|
| 1) |
Some antigens require heat induced antigen retrieval procedure or prolonged reaction time with primary antibody, which may render the sections easily come off. |
|
| – |
Mount tissue sections on slides coated with an adhesive such as 0.02% poly-L-lysine or silane. |
|