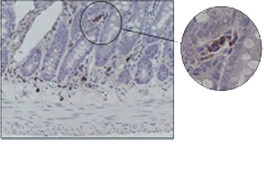
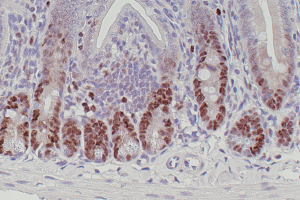
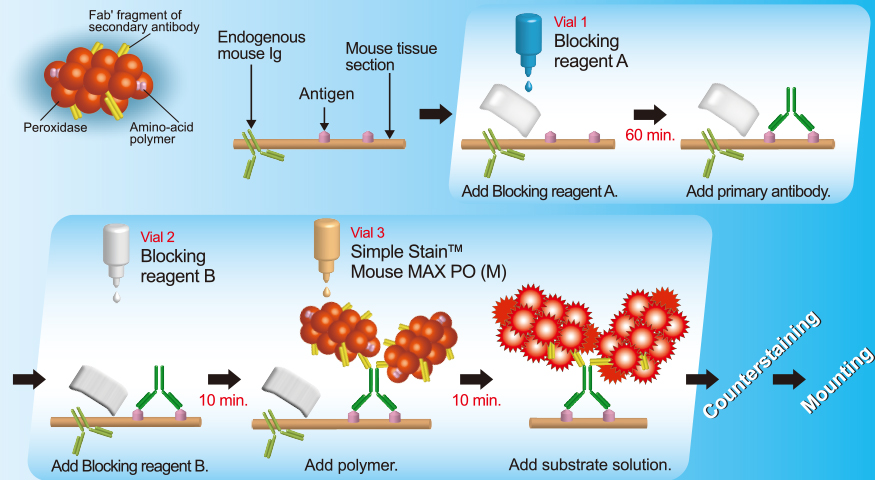
DETECTION SYSTEMS
For Animal tissue
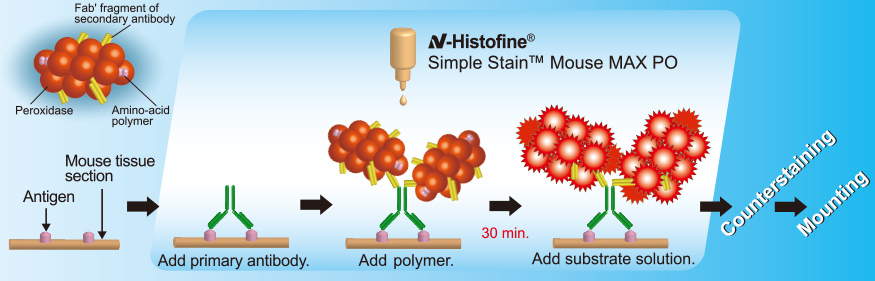
For Mouse
With mouse primary antibodies
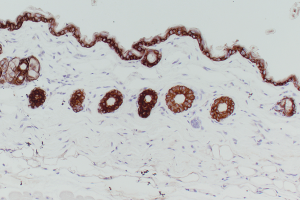
With rabbit, goat or rat primary antibodies
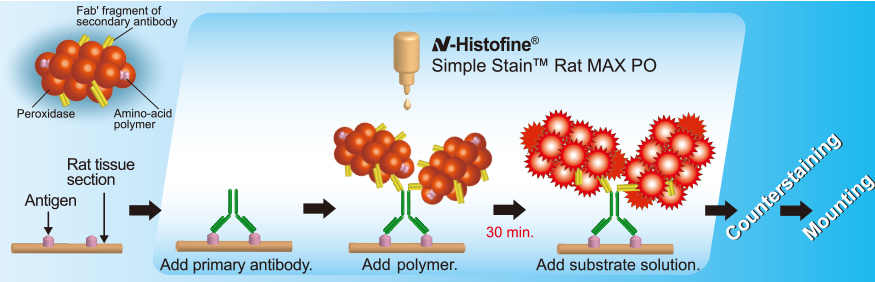
For Rat
With mouse, rabbit, or goat primary antibodies
Advantage
■ Technical Report
Reference
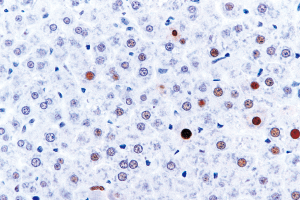
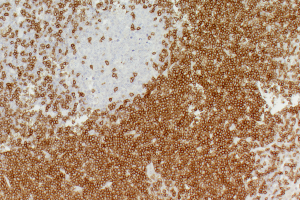
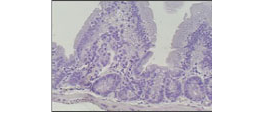
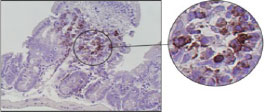
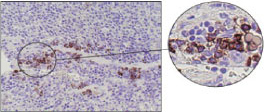
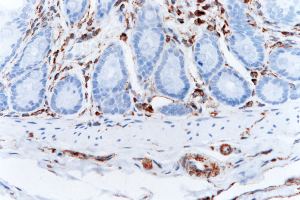
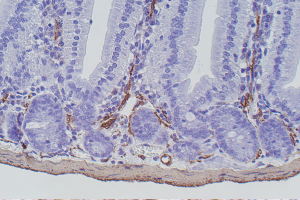
■ Mouse and Rat tissue Sections
- (1) Ezure, K., et al: Glycine Is Used as a Transmitter by Decrementing Expiratory Neurons of the Ventrolateral Medulla in the Rat. The Journal of Neuroscience 23: 8941– 8948, 2003.
- (2) Kitada, M., et al: Translocation of Glomerular p47phox and p67phox by Protein Kinase C-β Activation Is Required for Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 52: 2603–2614, 2003.
- (3) Matsuyoshi, H., et al: Enhanced Priming of Antigen-Specific CTLs In Vivo by Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Dendritic Cells Expressing Chemokine Along with Antigenic Protein: Application to Antitumor Vaccination. The Journal of Immunology 172: 776-786, 2004.
- (4) Noiri E., et al: Oxidative and nitrosative stress in acute renal ischemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 281: 948-957, 2001.
- (5) Kazuyo, M., et al: Innate production of TH2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit+Sca-1+ lymphoid cells. NATURE. doi:10.1038/nature08636,2009.
×

×

×